What is medicinal cannabis?
Medicinal cannabis products are legal, high-quality medicines that can be prescribed by a doctor. Medicinal cannabis is derived from the cannabis plant and can be used to treat the symptoms of certain diseases and the side effects of certain treatments.
There are various medicinal cannabis products available to treat different conditions. The active ingredients in medicinal cannabis are called "cannabinoids". There are between 80 and 100 cannabinoids in medicinal cannabis, and researchers are still learning how they all work.
Currently, most medicinal cannabis products contain the cannabinoids cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC).
What are the benefits of medicinal THC?
There are currently different manufactured versions of marijuana. Doctors usually prescribe them to treat severe epilepsy or side effects of chemotherapy.
The following list of uses of medicinal THC in Switzerland is among the most discussed in scientific research.
pain management
The cannabinoids in cannabis can reduce pain by altering the pathways of pain perception in the brain. This can be helpful in treating conditions that cause chronic pain, such as:
arthritis
fibromyalgia
endometriosis
migraine
It can also minimize the side effects of cancer treatment, such as loss of appetite. In some cases, medical marijuana can reportedly replace long-term use of anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen, which can have many negative side effects.
anti-inflammatories
The CBD found in marijuana is believed to help reduce inflammation. In theory, this could primarily benefit inflammatory conditions, such as:
Crohn's disease
irritable bowel syndrome
Rheumatoid arthritis
Reducing inflammation in the body can also improve overall health.
Neurological and mental disorders
Because of its effects on the limbic system, doctors sometimes prescribe medicinal cannabis to treat the following mental and neurological conditions:
anxiety states
epilepsy
multiple sclerosis
Parkinson's disease
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Tourette syndrome
sleep management
The relaxing and relaxing effects of cannabis can help improve sleep disorders such as chronic insomnia. Better sleep may subsequently occur when pain is reduced through marijuana use.
According to the latest findings, it is assumed that the sleep-promoting effect of cannabis is due to its interaction with the cannabinoid receptors in the brain. When cannabinoids bind to these receptors, they send out neural messages that increase sleep-inducing adenosine levels and suppress the brain's arousal system. Together, these two effects can contribute to users feeling sedated and increased sleepiness.
Cannabis and its history
Cannabis already has a very eventful history behind it. It was banned from official pharmacopoeias in the early part of the 20th century and banned by the 1951 Federal Narcotics Act. In the 19th century, cannabis came to us from India and spread widely throughout Europe and the West. It has been applied in different ways. It was used to treat migraines, pain, whooping cough, asthma or as a sedative and sleeping pill. In the 1930s, repressive measures around the world caused cannabis and numerous other substances to lose their status as medicines and were subsequently declared illegal drugs. In Switzerland, too, this movement ultimately led to the Federal Narcotics Act banning the use of cannabis in principle.
The plant and its active ingredients
The plant was used in various forms throughout the 20th century to improve mood. However, the use of medicinal cannabis was completely forbidden. The discovery of the endocannabinoid receptors in the late 1980's and 1990's reignited interest in its many therapeutic abilities. In short, the Cannabis sativa plant and its derivatives contain substances called cannabinoids. The best known and best studied are cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), which act on these receptors. THC is described as a psychoactive substance and is responsible for the well-known euphoric effects of cannabis. The CBD, however, is not psychoactive and therefore legally available. In Switzerland, drugs with a THC content of less than 1% are legal and therefore not subject to the Narcotics Act.
Medical use of THC in Switzerland
Cannabis is classified as a prohibited narcotic in Switzerland. However, the ban on medicinal cannabis was lifted in August 2022. That is why our company was one of the first companies to turn to the production of medicinal cannabis.
Cannabis medicinal products are the entirety of the marijuana products used, including flowers. In Switzerland, any licensed doctor can prescribe cannabis medicinal products for the patient. These are referred to as so-called "magistral formulations". These are remedies that are issued by a pharmacy on the prescription of a doctor.
Lifting the ban for medical purposes
The growing interest in cannabis medicines has increased significantly in recent years due to the wide range of possible uses. For this reason, in August 2022, Parliament lifted the ban on cannabis for medical purposes in the Narcotics Act. For this reason, an exceptional permit is no longer required for the medical prescription of cannabis medicinal products. During the first two years of treatment, the doctor treating you must submit and report therapy data to the Federal Office of Public Health.
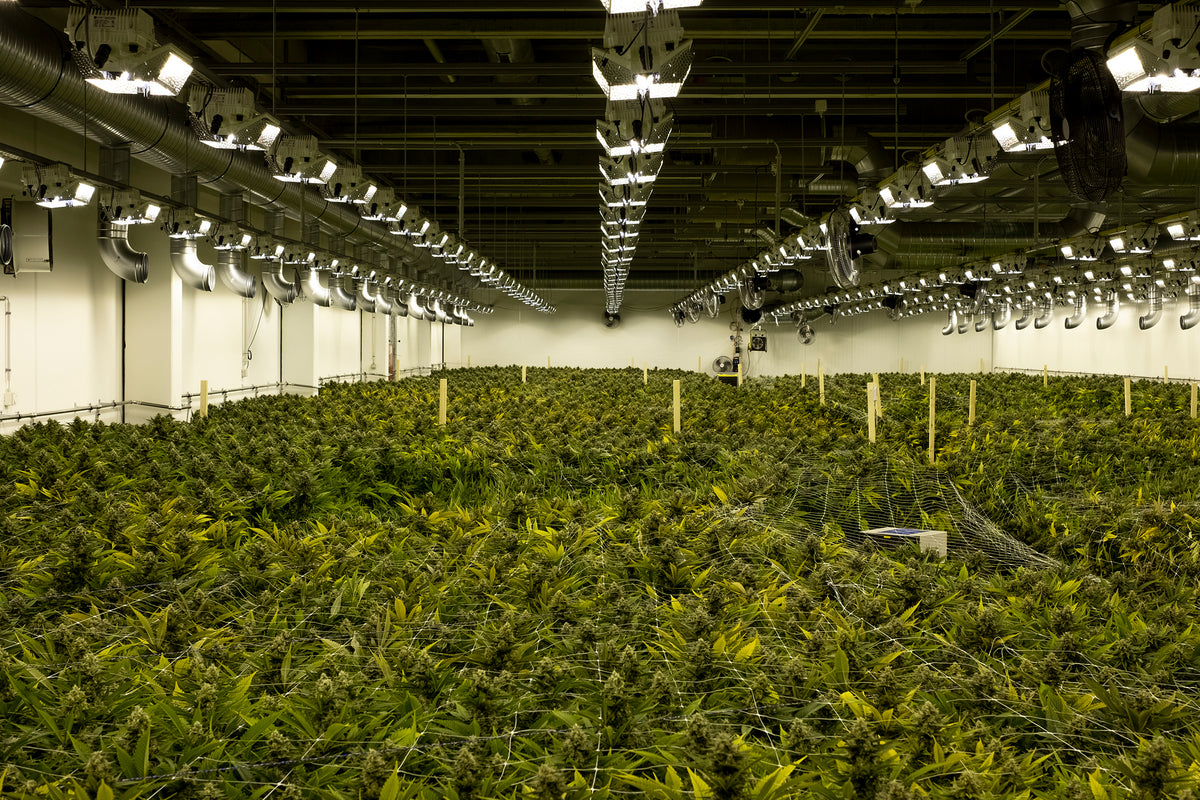
As a result of this change in the law, the cultivation, processing, production and trading of cannabis for medical purposes was subject to the Swissmedic control system.
Government control of medicinal THC cultivation
The product quality of the plants and plant extracts is essential for the success of treatment with cannabis medicinal products. The cultivation of cannabis for medical purposes should be made possible for coverage with cannabis medicinal products of standardized quality in Switzerland. In addition to the provisions of the Swiss Narcotics Act, the internationally binding provisions on narcotics must be observed. These regulations stipulate that cannabis cultivation is subject to state supervision. Swissmedic assumes the task of controlling and monitoring cultivation for medical purposes in Switzerland. State-controlled cultivation has only recently taken place in Switzerland, with Sainfortall fulfilling and testing important requirements.